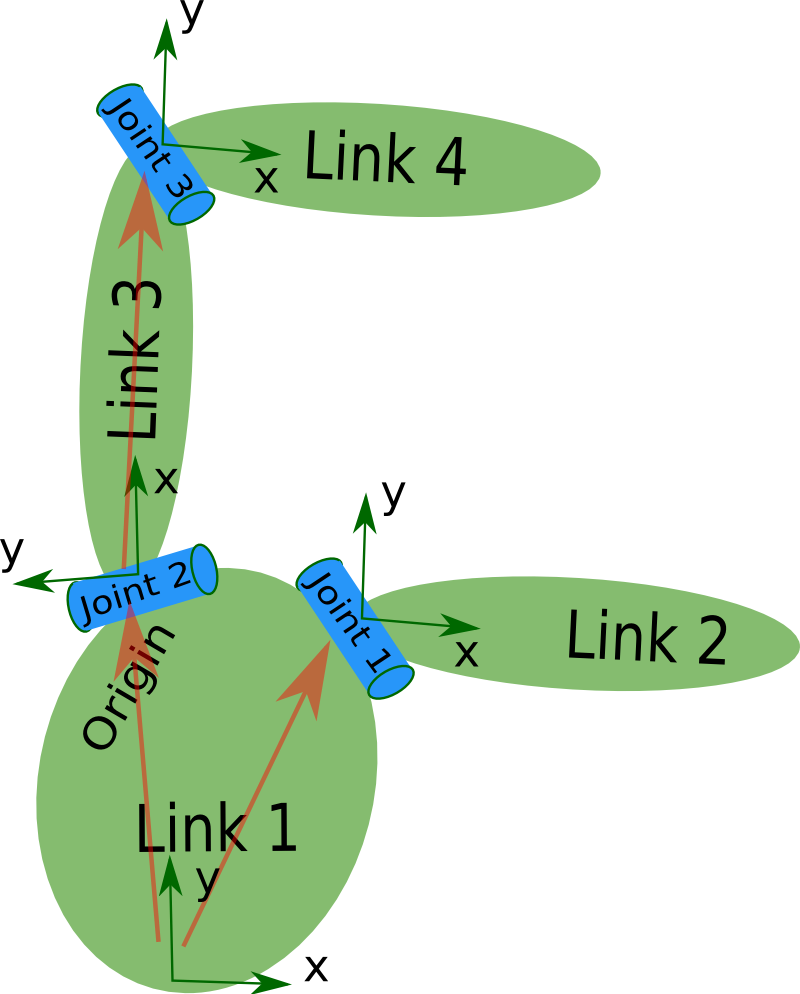
1 概述 机器人都是由link和joint进行描述.
2 流程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 mkdir -p urdf_ws/srccd urdf_ws/srcros2 pkg create --build-type ament_cmake --dependencies urdf robot_state_publisher --license Apache-2.0 my_robot_description cd my_robot_descriptionmkdir -p urdf
写入urdf代码.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 <?xml version="1.0" ?> <robot name="my_robot" > <link name="base_link" > <visual> <geometry> <box size="0.2 0.2 0.05" /> </geometry> <origin xyz="0 0 0.025" /> <material name="blue" > <color rgba="0 0 1 1" /> </material> </visual> </link> <joint name="joint1" type ="fixed" > <parent link ="base_link" /> <child link ="link1" /> <origin xyz="0 0 0.05" rpy="0 0 0" /> <axis xyz="0 0 1" /> <limit lower="-1.57" upper="1.57" effort="1.0" velocity="1.0" /> </joint> <link name="link1" > <visual> <geometry> <cylinder length="0.4" radius="0.03" /> </geometry> <origin xyz="0 0 0.2" rpy="0 0 0" /> <material name="green" > <color rgba="0 1 0 1" /> </material> </visual> </link> <joint name="joint2" type ="fixed" > <parent link ="link1" /> <child link ="link2" /> <origin xyz="0 0 0.4" rpy="0 0 0" /> <axis xyz="0 1 0" /> <limit lower="-1.57" upper="1.57" effort="1.0" velocity="1.0" /> </joint> <link name="link2" > <visual> <geometry> <cylinder length="0.3" radius="0.02" /> </geometry> <origin xyz="0 0 0.15" rpy="0 0 0" /> <material name="red" > <color rgba="1 0 0 1" /> </material> </visual> </link> </robot>
编译并构建.
1 2 colcon build source install/setup.bash
创建 launch 目录, 在其中编写 launch.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 from launch import LaunchDescription from launch.actions import DeclareLaunchArgument from launch.substitutions import LaunchConfiguration, Command from launch_ros.actions import Node from launch_ros.parameter_descriptions import ParameterValue from ament_index_python.packages import get_package_share_directory import os def generate_launch_description(): pkg_path = get_package_share_directory('my_robot_description' ) default_model_path = os.path.join(pkg_path, 'urdf' , 'robot.urdf' ) rviz_config_path = os.path.join(pkg_path, 'config' , 'display_config.rviz' ) declare_model_arg_path = DeclareLaunchArgument( name='model' , default_value=str(default_model_path), description='Absolute path to robot urdf or xacro file' ) robot_description_result = Command(['xacro ' , LaunchConfiguration('model' )]) robot_description_val = ParameterValue(robot_description_result, value_type=str) return LaunchDescription([ declare_model_arg_path, Node( package='robot_state_publisher' , executable='robot_state_publisher' , parameters=[{'robot_description' : robot_description_val}], ), Node( package='joint_state_publisher_gui' , executable='joint_state_publisher_gui' , ), Node( package='rviz2' , executable='rviz2' , arguments=['-d' , rviz_config_path], ) ])
添加安装指令.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 install(DIRECTORY urdf DESTINATION share/${PROJECT_NAME} ) install(DIRECTORY launch DESTINATION share/${PROJECT_NAME} ) install(DIRECTORY config DESTINATION share/${PROJECT_NAME} )
目录结构如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 build install log src/ └── my_robot_description ├── CMakeLists.txt ├── include │ └── my_robot_description ├── launch │ └── display.launch.py │── config │ └── display_config.rviz ├── LICENSE ├── package.xml ├── src └── urdf └── robot.urdf
3 描述机器人关系的组件 3.1 robot_state_publisher
输入
输出: /tf 和 /tf_static:每个 link 的位置变换
3.2 joint_state_publisher /joint_states: 消息类型为 sensor_msgs/JointState
组件
功能说明
joint_state_publisher自动发布所有关节角度为 0 的状态
joint_state_publisher_gui提供滑块 GUI 让你拖动角度
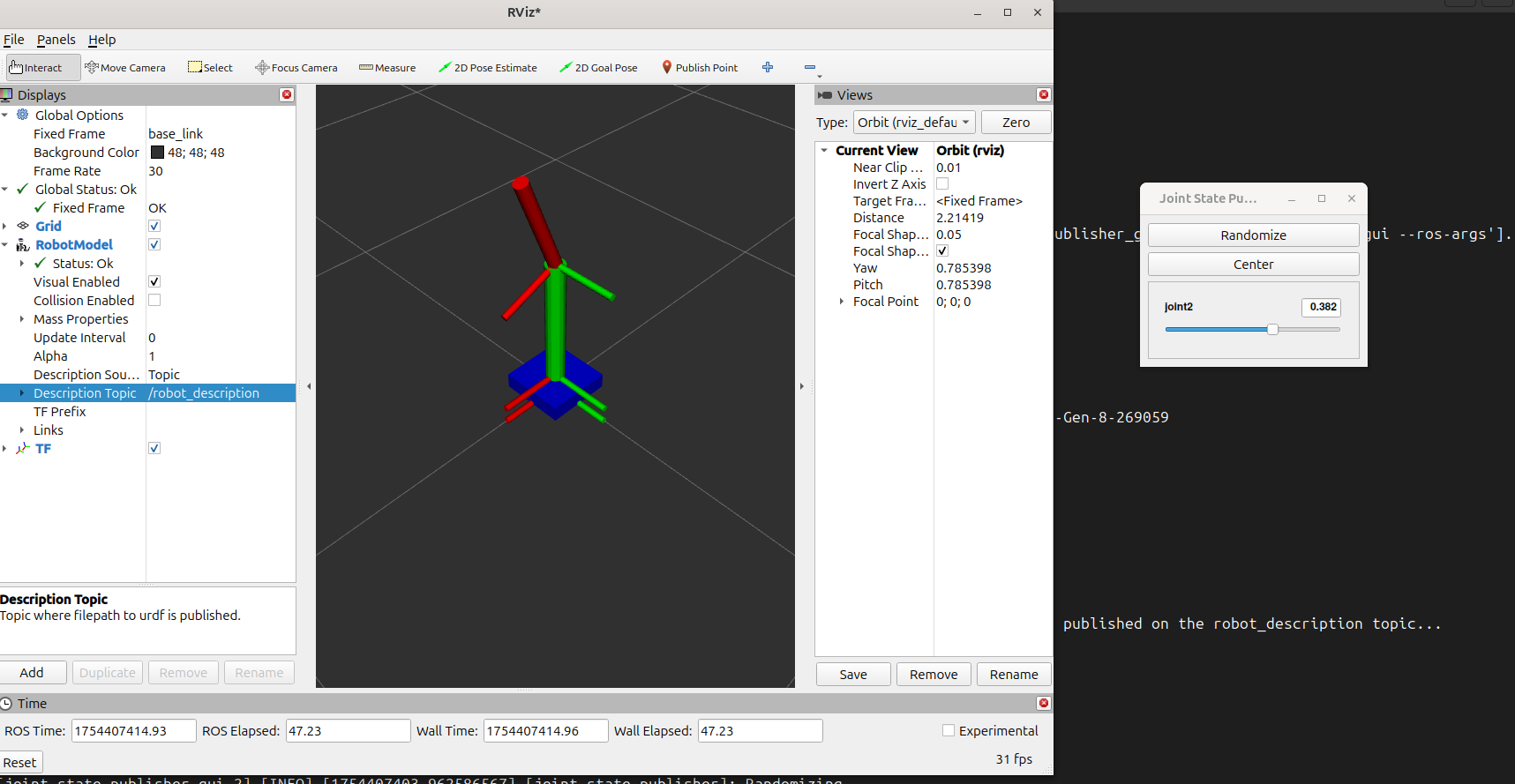
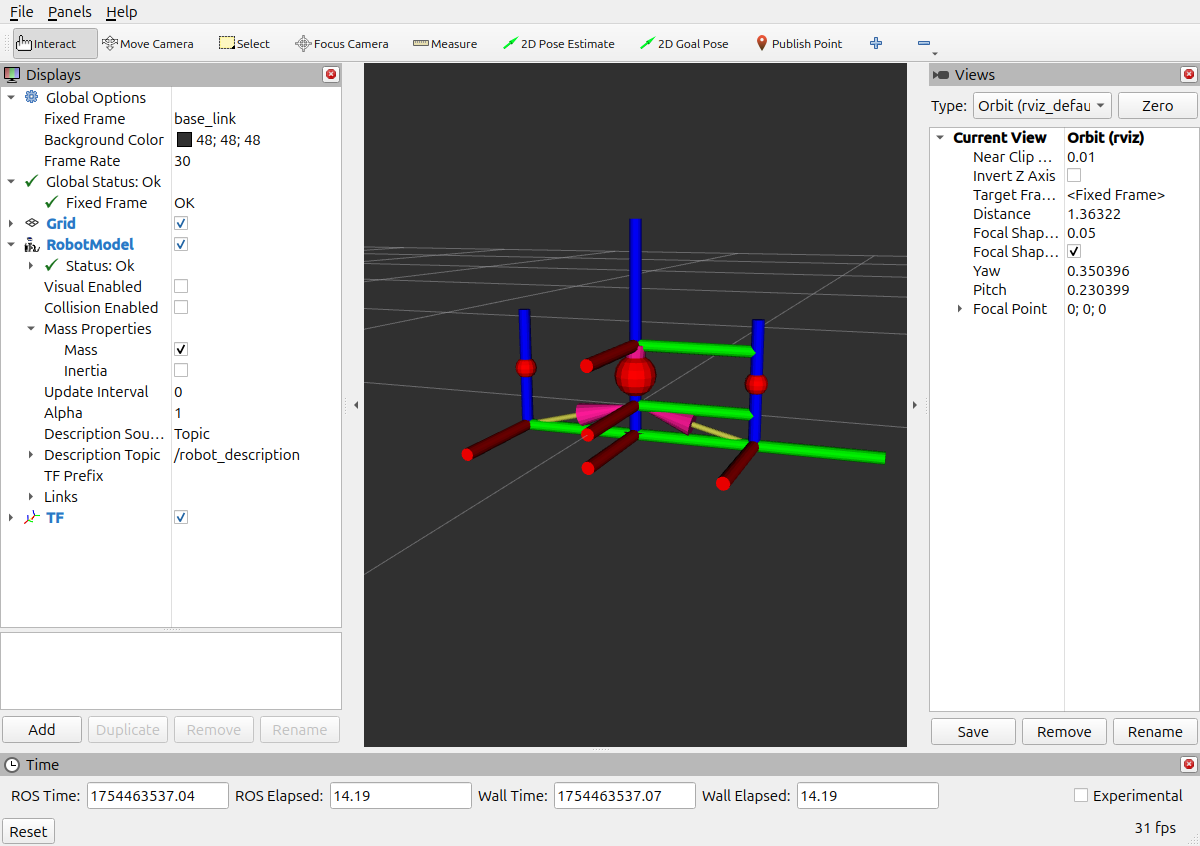
joint_state_publisher_gui 的效果, 如果 joint 的关系是 revolute, 则可以滑动.
4 xacro xacro 是对 urdf 的语法增强.
我们将上面的 urdf 换成 xacro 版本.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 <?xml version="1.0" ?> <robot xmlns:xacro="http://ros.org/wiki/xacro" name="my_robot" > <!-- 定义颜色 --> <xacro:property name="blue" value="0 0 1 1" /> <xacro:property name="green" value="0 1 0 1" /> <xacro:property name="red" value="1 0 0 1" /> <!-- 定义基本尺寸参数 --> <xacro:property name="base_size" value="0.2 0.2 0.05" /> <xacro:property name="link1_length" value="0.4" /> <xacro:property name="link2_length" value="0.3" /> <link name="base_link" > <visual> <geometry> <box size="${base_size} " /> </geometry> <origin xyz="0 0 0.025" /> <material name="blue" > <color rgba="${blue} " /> </material> </visual> </link> <joint name="joint1" type ="fixed" > <parent link ="base_link" /> <child link ="link1" /> <origin xyz="0 0 0.05" rpy="0 0 0" /> </joint> <link name="link1" > <visual> <geometry> <cylinder length="${link1_length} " radius="0.03" /> </geometry> <origin xyz="0 0 ${link1_length/2} " rpy="0 0 0" /> <material name="green" > <color rgba="${green} " /> </material> </visual> </link> <joint name="joint2" type ="revolute" > <parent link ="link1" /> <child link ="link2" /> <origin xyz="0 0 ${link1_length} " rpy="0 0 0" /> <axis xyz="0 1 0" /> <limit lower="-1.57" upper="1.57" effort="1.0" velocity="1.0" /> </joint> <link name="link2" > <visual> <geometry> <cylinder length="${link2_length} " radius="0.02" /> </geometry> <origin xyz="0 0 ${link2_length/2} " rpy="0 0 0" /> <material name="red" > <color rgba="${red} " /> </material> </visual> </link> </robot>
4.1 xacro 的多文件结构
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 urdf/ ├── base.xacro ├── macros.xacro ├── robot.xacro ├── robot.urdf ├── sensors.xacro └── wheels.xacro
我们传入 robot.xacro 即可, xacro 会自动解析所有 include 文件.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 <?xml version="1.0" ?> <robot xmlns:xacro="http://ros.org/wiki/xacro" name="my_wheeled_robot" > <!-- Include modules --> <xacro:include filename="macros.xacro" /> <xacro:include filename="base.xacro" /> <xacro:include filename="wheels.xacro" /> <xacro:include filename="sensors.xacro" /> <!-- Define properties (used as macro arguments) --> <xacro:property name="base_size" value="0.4 0.4 0.1" /> <!-- Call base macro with required params --> <xacro:base_link base_size="${base_size} " /> <!-- Wheels --> <xacro:wheel name="left_wheel" parent="base_link" xyz="0.1 0.2 0" /> <xacro:wheel name="right_wheel" parent="base_link" xyz="0.1 -0.2 0" /> <!-- Sensor --> <xacro:lidar_sensor parent="base_link" xyz="0 0 0.1" /> </robot>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 <?xml version="1.0" ?> <robot xmlns:xacro="http://ros.org/wiki/xacro" > <!-- 颜色 --> <xacro:property name="color_red" value="1 0 0 1" /> <xacro:property name="color_green" value="0 1 0 1" /> <xacro:property name="color_blue" value="0 0 1 1" /> <!-- 底盘尺寸 --> <xacro:property name="base_size" value="0.4 0.3 0.1" /> <xacro:property name="wheel_radius" value="0.05" /> <xacro:property name="wheel_width" value="0.02" /> </robot>
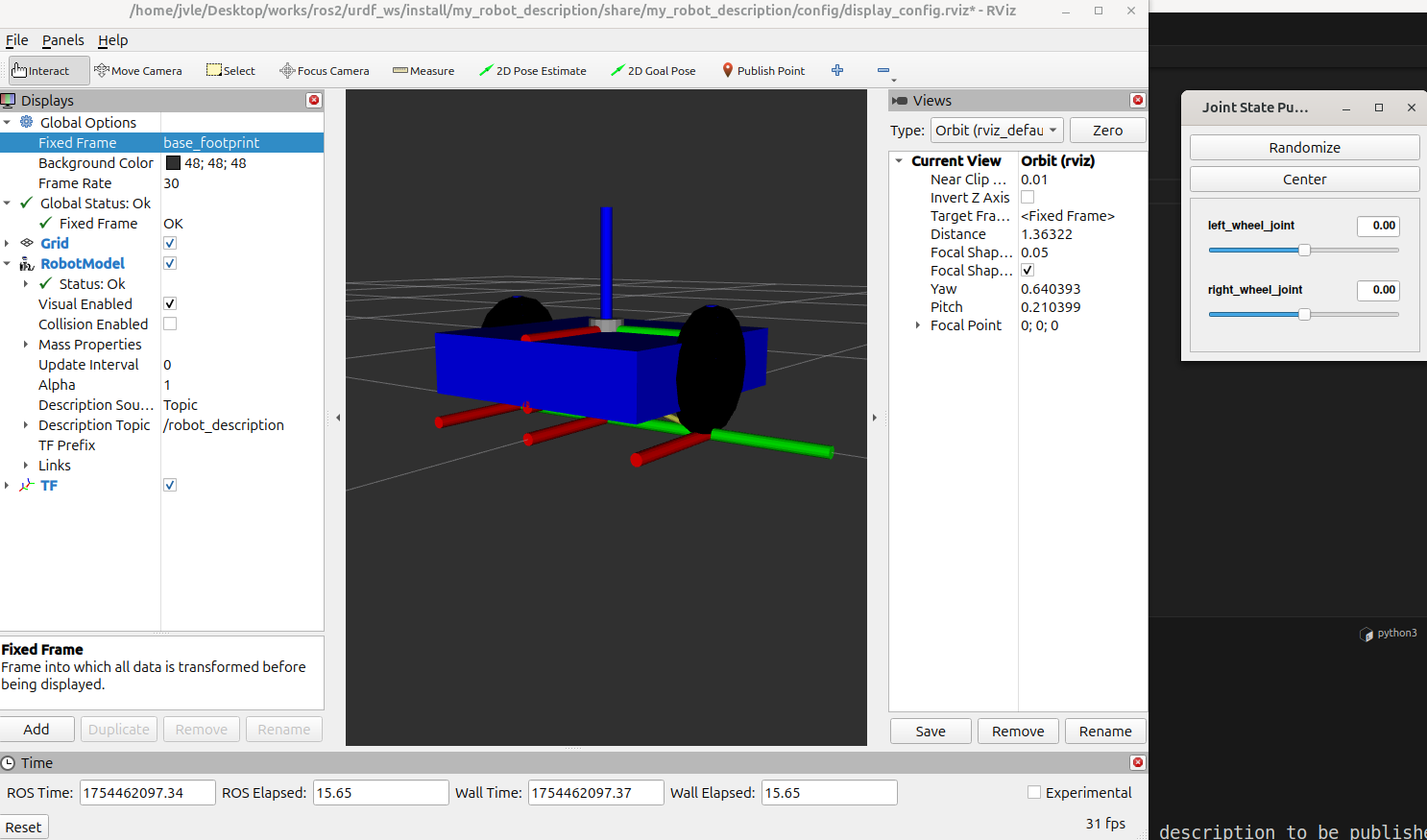
对于 base.xacro 我们可以建立一个虚拟组件对地面进行贴合.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 <?xml version="1.0" ?> <robot xmlns:xacro="http://ros.org/wiki/xacro" > <xacro:macro name="base_link" params="base_size" > <xacro:property name="base_size_z" value="${float(base_size.split()[2])} " /> <link name="base_footprint" /> <link name="base_link" > <visual> <geometry> <box size="${base_size} " /> </geometry> <origin xyz="0 0 ${base_size_z / 2} " /> <material name="blue" > <color rgba="${color_blue} " /> </material> </visual> <collision> <geometry> <box size="${base_size} " /> </geometry> <origin xyz="0 0 ${base_size_z / 2} " /> <material name="blue" > <color rgba="${color_blue} " /> </material> </collision> </link> <joint name="joint_name" type ="fixed" > <origin xyz="0 0 ${base_size_z / 2} " rpy="0 0 0" /> <parent link ="base_footprint" /> <child link ="base_link" /> </joint> </xacro:macro> </robot>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 <?xml version="1.0" ?> <robot xmlns:xacro="http://ros.org/wiki/xacro" > <xacro:macro name="mul_wheel" params="name parent xyz" > <xacro:property name="wheel_mass" value="0.1" /> <link name="${name} _link" > <visual> <geometry> <sphere radius="${wheel_radius} " /> </geometry> <origin xyz="0 0 ${wheel_radius} " rpy="0 0 0" /> <material name="gray" > <color rgba="0.4 0.4 0.4 1" /> </material> </visual> <collision> <geometry> <sphere radius="${wheel_radius} " /> </geometry> <origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" /> </collision> <inertial> <origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" /> <mass value="${wheel_mass} " /> <inertia ixx="1e-5" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0" iyy="1e-5" iyz="0.0" izz="1e-5" /> </inertial> </link> <joint name="${name} _joint" type ="fixed" > <parent link ="${parent} " /> <child link ="${name} _link" /> <origin xyz="${xyz} " rpy="0 0 0" /> </joint> </xacro:macro> <xacro:macro name="wheel" params="name parent xyz" > <xacro:property name="wheel_mass" value="0.3" /> <xacro:property name="inertia_ixx" value="${0.5 * wheel_mass * wheel_radius * wheel_radius} " /> <xacro:property name="inertia_iyy" value="${0.5 * wheel_mass * wheel_radius * wheel_radius} " /> <xacro:property name="inertia_izz" value="${0.5 * wheel_mass * wheel_radius * wheel_radius} " /> <link name="${name} _link" > <visual> <geometry> <cylinder radius="${wheel_radius} " length="${wheel_width} " /> </geometry> <origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="1.5708 0 0" /> <material name="black" > <color rgba="0 0 0 1" /> </material> </visual> <collision> <geometry> <cylinder radius="${wheel_radius} " length="${wheel_width} " /> </geometry> <origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="1.5708 0 0" /> <material name="black" > <color rgba="0 0 0 1" /> </material> </collision> <inertial> <origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" /> <mass value="${wheel_mass} " /> <inertia ixx="${inertia_ixx} " ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0" iyy="${inertia_iyy} " iyz="0.0" izz="${inertia_izz} " /> </inertial> </link> <joint name="${name} _joint" type ="continuous" > <parent link ="${parent} " /> <child link ="${name} _link" /> <origin xyz="${xyz} " rpy="0 0 0" /> <axis xyz="0 1 0" /> </joint> </xacro:macro> </robot>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 <?xml version="1.0" ?> <robot xmlns:xacro="http://ros.org/wiki/xacro" > <xacro:macro name="lidar_sensor" params="parent xyz" > <link name="lidar_link" > <visual> <geometry> <cylinder radius="0.03" length="0.02" /> </geometry> <origin xyz="0 0 0.01" rpy="0 0 0" /> <material name="gray" > <color rgba="0.6 0.6 0.6 1" /> </material> </visual> </link> <joint name="lidar_joint" type ="fixed" > <parent link ="${parent} " /> <child link ="lidar_link" /> <origin xyz="${xyz} " rpy="0 0 0" /> </joint> </xacro:macro> </robot>
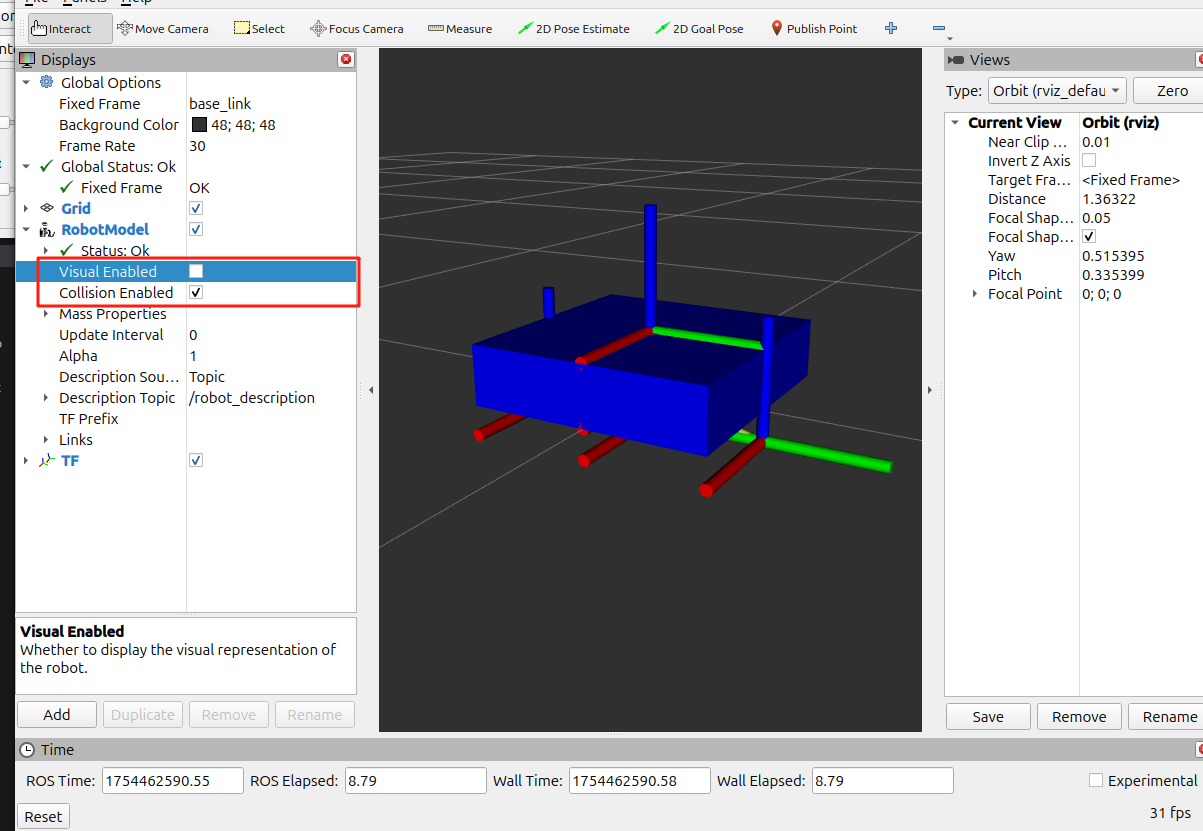
5 物理属性 5.1 碰撞 collision 标签可以给组件添加碰撞体积, 一般写法与 visual 一致, 对于不规则的物体我们也可以用 collision 将碰撞体积近似.
这里详见 base.xacro 和 wheels.xacro 的写法.
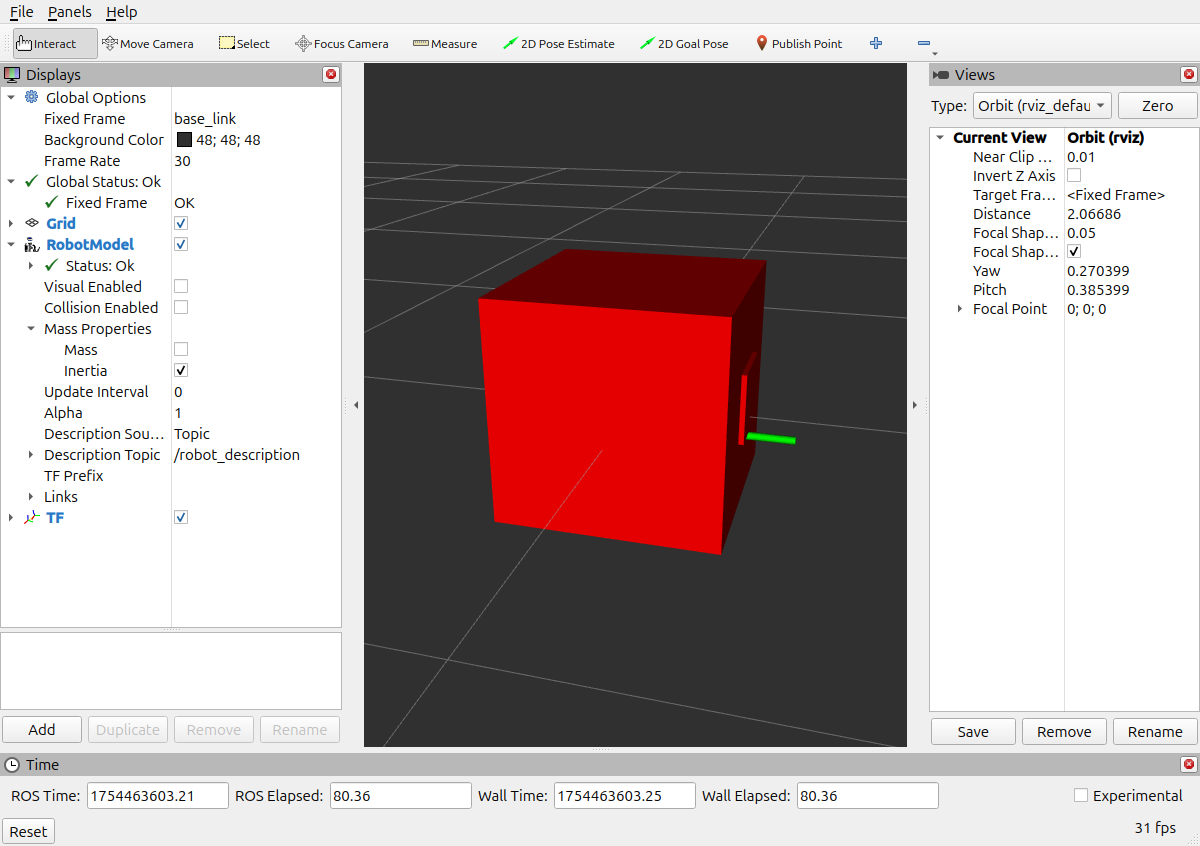
通过开关我们可以看到碰撞体积, 比如这里只写了 base.xacro 的碰撞体积.
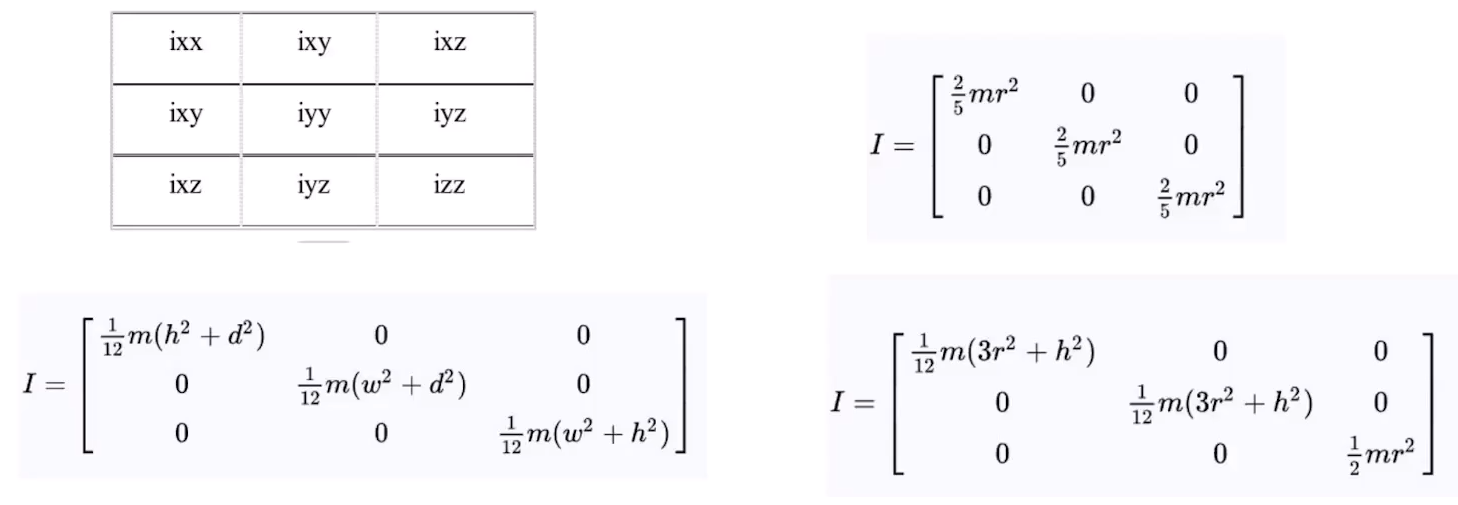
5.2 惯性 这里可以查看 base.xacro 为例.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 <link name="base_link" > <visual> <geometry> <cylinder length="0.6" radius="0.2" /> </geometry> <material name="blue" > <color rgba="0 0 .8 1" /> </material> </visual> <collision> <geometry> <cylinder length="0.6" radius="0.2" /> </geometry> </collision> <inertial> <mass value="10" /> <inertia ixx="0.4" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0" iyy="0.4" iyz="0.0" izz="0.2" /> </inertial> </link>
这里可以看一下 base.xacro 和 wheels.xacro.
6 References